概述
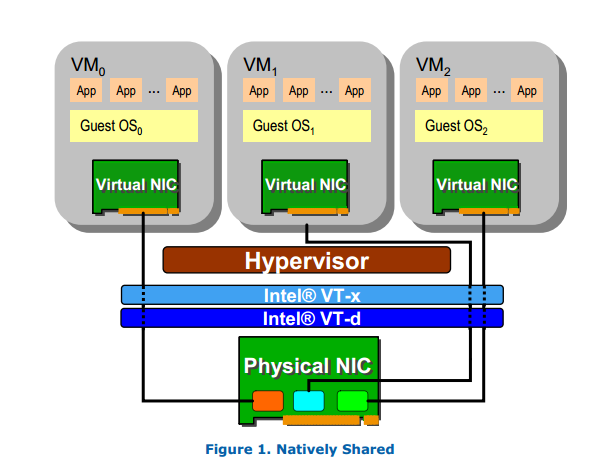
SR-IOV 技术是一种基于硬件的虚拟化解决方案,可提高性能和可伸缩性。SR-IOV 标准允许在虚拟机之间高效共享 PCIe(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express,快速外设组件互连)设备,并且它是在硬件中实现的,可以获得能够与本机性能媲美的 I/O 性能。SR-IOV 规范(Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing specification)定义了新的标准,根据该标准,创建的新设备可允许VM不通过Hypervisor,而直接连接到 I/O 设备。本地共享设备会为每个接口提供单独的内存空间,工作队列。参考
PCI-SIG SR-IOV1 标准目的在于标准化 在虚拟环境中共享一个 I/O 设备的方式。这个目标绕开了Hypervisor 的参与,提供了独立的内存空间、中断、DMA 流给每一个虚拟机用于数据的通信。 SR-IOV 引入了两种新的function 类型:
- Physical Function(PF):这是一个拥有所用PCIe 功能的fucntion,当然也包含了SR-IOV 扩展的能力
- Virtual Function (VF): 这是一个轻量级的PCIe
- function,包含了数据通信所需的资源。具有一个PCI总线中唯一的BDF识别号,这也是VF上DMA操作时硬件用来 作为向 PCIe总线发送访问请求的识别号。
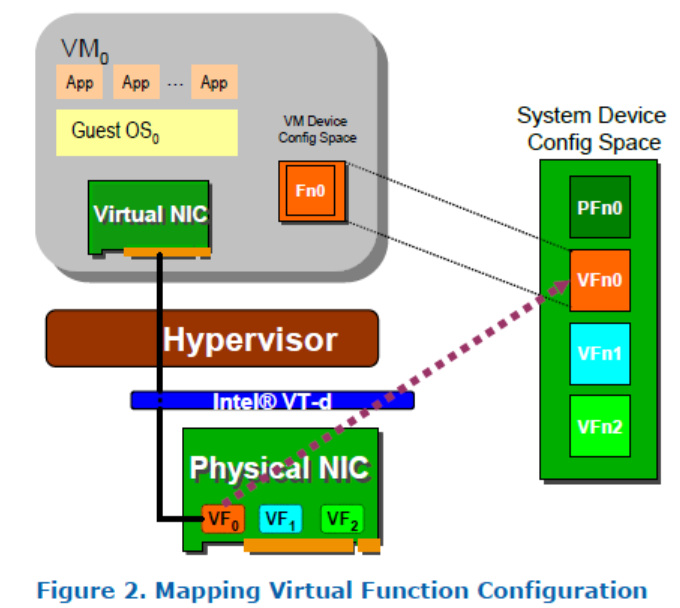
一个支持SR-IOV 的设备能够通过设置(一般由Hypervisor来配置)PCI的配置空间使其支持多个Function。每个Function都拥有自己的配置空间,拥有自己的基地址寄存器(BAR)。
PCIe 设备配置空间访问
设备的SR-IOV能力是通过配置空间进行配置的。
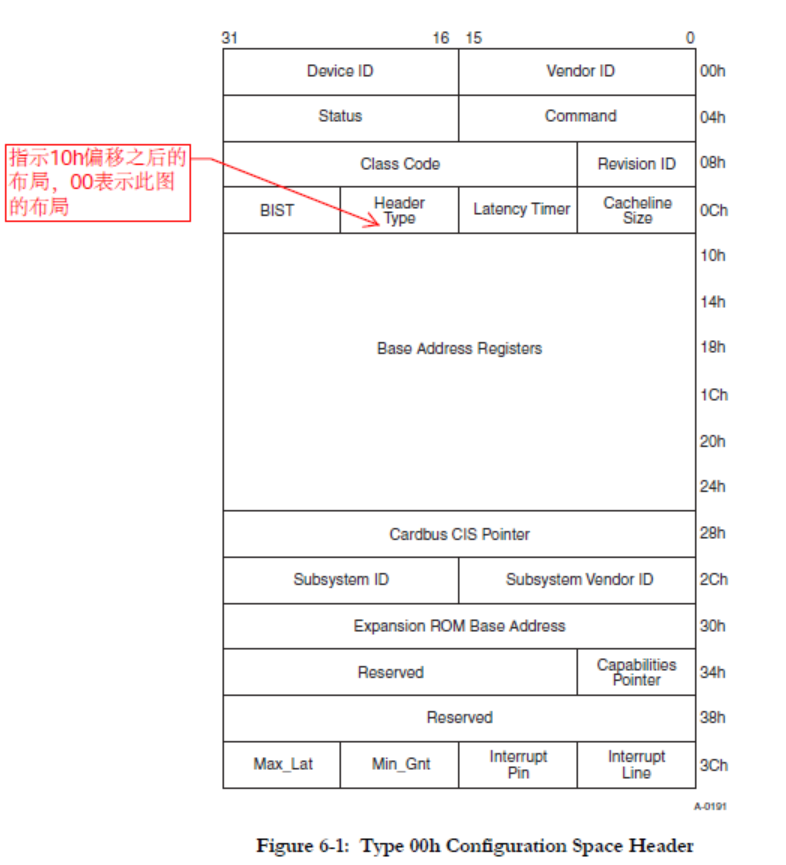
以内存映射的方式读取配置空间中的值
int pci_mmcfg_read(unsigned int seg, unsigned int bus,
unsigned int devfn, int reg, int len, u32 *value)
{
...
// 根据seg和bdf获取设备配置空间地址
// addr指向Configuration Space Header
// 参考 PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 3.0, 6.1
addr = pci_dev_base(seg, bus, devfn);
if (!addr)
goto err;
switch (len) {
case 1:
// reg为Configuration Space的域偏移
// 以内存映射方式读取设备配置空间的值
*value = mmio_config_readb(addr + reg);
break;
case 2:
*value = mmio_config_readw(addr + reg);
break;
case 4:
*value = mmio_config_readl(addr + reg);
break;
}
return 0;
}
根据bdf计算设备配置空间地址的算法 :
static char __iomem *pci_dev_base(unsigned int seg, unsigned int bus, unsigned int devfn)
{
char __iomem *addr;
addr = get_virt(seg, &bus);
if (!addr)
return NULL;
// 通过bdf定位到设置的配置地址空间在当前域地址空间 中的VA
return addr + ((bus << 20) | (devfn << 12));
}
get_virt是遍历 系统启动时获取的 MCFG Table(一个ACPI表,参考PCI Firmware Specification Revision 3.2, 4.1.2, Table 4-3),根据segment和bdf找到设备配置空间在当前domain下的VA.
static char __iomem *get_virt(unsigned int seg, unsigned int *bus)
{
struct acpi_mcfg_allocation *cfg;
int cfg_num;
for (cfg_num = 0; cfg_num < pci_mmcfg_config_num; cfg_num++) {
//取出Memory Mapped Enhanced Configuration Space Base Address Allocation Structure
// 结构体参考 PCI Firmware Specification Revision 3.2, 4.1.2, Table 4-3
cfg = pci_mmcfg_virt[cfg_num].cfg;
if (cfg->pci_segment == seg &&
(cfg->start_bus_number <= *bus) &&
(cfg->end_bus_number >= *bus)) {
*bus -= cfg->start_bus_number;
// 返回设备 配置空间
// (The base address field provides the 64-bit physical address of
// the base of the memory mapped configuration space associated
// with the PCI Segment Group.)
// 在当前domain地址空间中的 VA
return pci_mmcfg_virt[cfg_num].virt;
}
}
/* Fall back to type 0 */
return NULL;
}
上面函数中pci_mmcfg_virt[cfg_num].virt在是系统启动时通过mcfg_ioremap将第idx个mmcfg结构体(解析ACPI表得到)对应的配置空间映射到当前domain中的virt地址处。
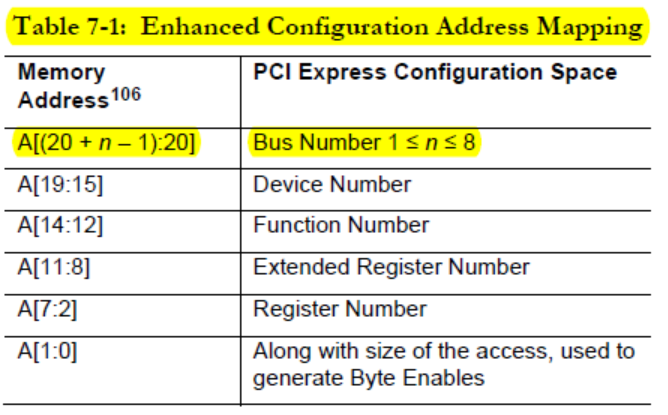
// 映射第idx个mmcfg结构体对应的配置空间对当前domain中的virt地址处
static void __iomem *mcfg_ioremap(const struct acpi_mcfg_allocation *cfg,
unsigned long idx, unsigned int prot)
{
unsigned long virt, size;
virt = PCI_MCFG_VIRT_START + (idx << mmcfg_pci_segment_shift) +
(cfg->start_bus_number << 20);
size = (cfg->end_bus_number - cfg->start_bus_number + 1) << 20;
if (virt + size < virt || virt + size > PCI_MCFG_VIRT_END)
return NULL;
// 将mfn映射到hypervisor地址空间中的virt处
// cfg->address >> PAGE_SHIFT ,将PA右移PAGE_SHIFT之后等于物理页帧号mfn
// start_bus_number左移20,得到PA,再右移PAGE_SHITF得到bus相对address的偏移 按页对齐值
// 参考 PCI Express® Base Specification Revision 3.1a
// 7.2.2.PCI Express Enhanced Configuration Access Mechanism (ECAM)
if (map_pages_to_xen(virt,
(cfg->address >> PAGE_SHIFT) +
(cfg->start_bus_number << (20 - PAGE_SHIFT)),
size >> PAGE_SHIFT, prot))
return NULL;
return (void __iomem *) virt;
}
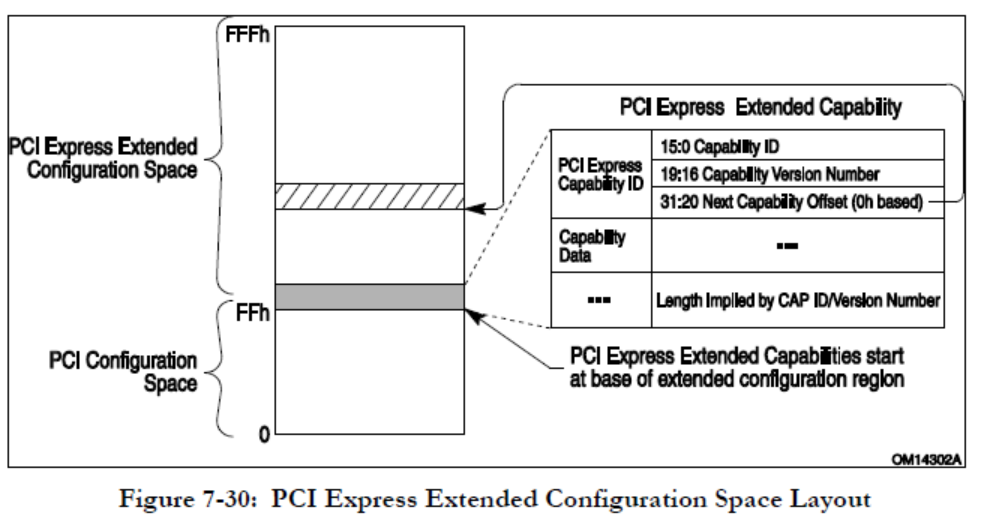
根据Figure 1可知,偏移0ffh处为PCI Express Extened Capability,而 Extended Capability ID为0010h是SR-IOV Extended Capability(参考Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing Specification Revision 1.1: 3.3),结构如下:
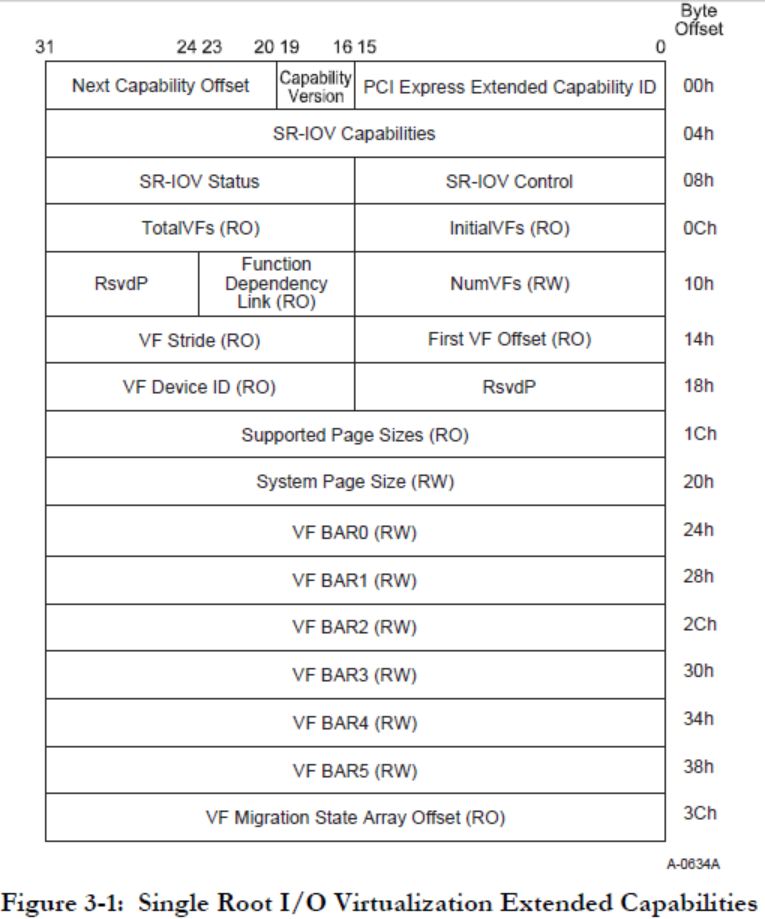
//根据cap ID查找 PCI Express Extended Capabilities
int pci_find_next_ext_capability(int seg, int bus, int devfn, int start, int cap)
{
u32 header;
int ttl = 480; /* 3840 bytes, minimum 8 bytes per capability */
int pos = max(start, 0x100);
// 读取配置空间中 PCI Express Extended Capabilities的偏移
// 参考PCI Express® Base Specification Revision 3.1a ,
// 7.9. PCI Express Extended Capabilities
header = pci_conf_read32(seg, bus, PCI_SLOT(devfn), PCI_FUNC(devfn), pos);
/*
* If we have no capabilities, this is indicated by cap ID,
* cap version and next pointer all being 0.
*/
if ( (header == 0) || (header == -1) )
return 0;
ASSERT(start != pos || PCI_EXT_CAP_ID(header) == cap);
while ( ttl-- > 0 ) {
if ( PCI_EXT_CAP_ID(header) == cap && pos != start )
return pos;
pos = PCI_EXT_CAP_NEXT(header);
if ( pos < 0x100 )
break;
header = pci_conf_read32(seg, bus, PCI_SLOT(devfn), PCI_FUNC(devfn), pos);
}
return 0;
}
通过上面函数可定位到设备配置空间的SR-IOV Extended Capability,之后就可以对设备的SR-IOV Capability进行操作。
int pci_add_device(u16 seg, u8 bus, u8 devfn, const struct pci_dev_info *info)
{
...
pdev = alloc_pdev(pseg, bus, devfn);
if ( !pdev )
goto out;
if ( info )
pdev->info = *info;
else if ( !pdev->vf_rlen[0] )
{
// 参考Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing Specification Revision 1.1
// 3.3 SR-IOV Extended Capability
// 定位到SR-IOV Extended Capability
unsigned int pos = pci_find_ext_capability(seg, bus, devfn,
PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_SRIOV);
// 参考SR-IOV手册3.3.3
u16 ctrl = pci_conf_read16(seg, bus, slot, func, pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL);
if ( !pos )
/* Nothing */;
//如果没有开启VF Enable和VF MSE
else if ( !(ctrl & (PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_VFE | PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_MSE)) )
{
unsigned int i;
BUILD_BUG_ON(ARRAY_SIZE(pdev->vf_rlen) != PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS);
for ( i = 0; i < PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS; ++i )
{
unsigned int idx = pos + PCI_SRIOV_BAR + i * 4;
//读取VF BAR (SR-IOV 3.3.14)
u32 bar = pci_conf_read32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx);
u32 hi = 0;
// 参考PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 3.0, 6.2.5.1. Address Maps
// 第0位为1,则为映射到I/O地址空间,VF BAR不支持此种映射方式
if ( (bar & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE) ==
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_IO )
{
printk(XENLOG_WARNING
"SR-IOV device %04x:%02x:%02x.%u with vf BAR%u"
" in IO space\n",
seg, bus, slot, func, i);
continue;
}
pci_conf_write32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx, ~0);
// 参考PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 3.0, 6.2.5.1. Address Maps
// Base register is 64 bits wide and can be mapped
// anywhere in the 64-bit address space
if ( (bar & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_MASK) ==
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_64 )
{
if ( i >= PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS )
{
printk(XENLOG_WARNING
"SR-IOV device %04x:%02x:%02x.%u with 64-bit"
" vf BAR in last slot\n",
seg, bus, slot, func);
break;
}
//读取VF BAR 高32位(SR-IOV 3.3.14)
hi = pci_conf_read32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx + 4);
pci_conf_write32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx + 4, ~0);
}
//PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 3.0, Figure 6-5:
//需要探测BAR空间的长度,方法是向BAR写全1,
//再读出清除标志位后,取反+1即是BAR地址空间大小
pdev->vf_rlen[i] = pci_conf_read32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx) &
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_MASK;
if ( (bar & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_MASK) ==
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_64 )
{
// 64位地址空间大小
pdev->vf_rlen[i] |= (u64)pci_conf_read32(seg, bus,
slot, func,
idx + 4) << 32;
//将BAR高32位原值写回
pci_conf_write32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx + 4, hi);
}
else if ( pdev->vf_rlen[i] )
// Base register is 32 bits
pdev->vf_rlen[i] |= (u64)~0 << 32;
//将BAR原值写回
pci_conf_write32(seg, bus, slot, func, idx, bar);
//BAR地址空间大小( 取反加一?)
pdev->vf_rlen[i] = -pdev->vf_rlen[i];
if ( (bar & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_MASK) ==
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_64 )
++i;// Base register is 64 bits,则i加一
}
}
else
printk(XENLOG_WARNING
"SR-IOV device %04x:%02x:%02x.%u has its virtual"
" functions already enabled (%04x)\n",
seg, bus, slot, func, ctrl);
}
...
}
PF Driver SR-IOV初始化
在domain 0下,系统 初始化时扫描所有pci设备: pci_legacy_init–>pcibios_scan_root–>pci_scan_root_bus->pci_scan_child_bus->pci_scan_slot–> pci_scan_single_device(pci_scan_device)–>pci_device_add –> pci_init_capabilities–>pci_iov_init–>sriov_init
// pos 指向 SR-IOV Extended Capability
static int sriov_init(struct pci_dev *dev, int pos)
{
int i;
int rc;
int nres;
u32 pgsz;
u16 ctrl, total, offset, stride;
struct pci_sriov *iov;
struct resource *res;
struct pci_dev *pdev;
if (pci_pcie_type(dev) != PCI_EXP_TYPE_RC_END &&
pci_pcie_type(dev) != PCI_EXP_TYPE_ENDPOINT)
return -ENODEV;
pci_read_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL, &ctrl);
if (ctrl & PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_VFE) {
// 如果开启了与PF关联的VFs,初始化时则复位
pci_write_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL, 0);
ssleep(1);
}
// 读取与PF关联的VFs的总数
pci_read_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_TOTAL_VF, &total);
if (!total)
return 0;
ctrl = 0;
list_for_each_entry(pdev, &dev->bus->devices, bus_list)
if (pdev->is_physfn)
goto found;
pdev = NULL;
if (pci_ari_enabled(dev->bus))
ctrl |= PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_ARI;
found:
pci_write_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL, ctrl);
pci_write_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_NUM_VF, 0);
// 读取第一个VF的Routing ID的偏移
pci_read_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_VF_OFFSET, &offset);
// VF的Routing ID 的Stride值
pci_read_config_word(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_VF_STRIDE, &stride);
if (!offset || (total > 1 && !stride))
return -EIO;
// PF支持的Page Size
pci_read_config_dword(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_SUP_PGSIZE, &pgsz);
i = PAGE_SHIFT > 12 ? PAGE_SHIFT - 12 : 0;
pgsz &= ~((1 << i) - 1);
if (!pgsz)
return -EIO;
pgsz &= ~(pgsz - 1);
pci_write_config_dword(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_SYS_PGSIZE, pgsz);
nres = 0;
for (i = 0; i < PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS; i++) {
res = dev->resource + PCI_IOV_RESOURCES + i;
// 读取VF BarN 的地址空间信息
// 如果返回1,则说明BAR是64位,占用两个VF BAR,即8个字节
i += __pci_read_base(dev, pci_bar_unknown, res,
pos + PCI_SRIOV_BAR + i * 4);
if (!res->flags)
continue;
// 如果BAR地址空间的大小 未按页对齐,则返回失败
if (resource_size(res) & (PAGE_SIZE - 1)) {
rc = -EIO;
goto failed;
}
res->end = res->start + resource_size(res) * total - 1;
nres++;
}
iov = kzalloc(sizeof(*iov), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!iov) {
rc = -ENOMEM;
goto failed;
}
//pos 指向 SR-IOV Extended Capability
iov->pos = pos;
//有效的VF个数
iov->nres = nres;
//SR-IOV Control fields
iov->ctrl = ctrl;
//VF总个数
iov->total_VFs = total;
//第一个VF的Routing ID的偏移
iov->offset = offset;
//VF的Routing ID 的Stride值
iov->stride = stride;
iov->pgsz = pgsz;
iov->self = dev;
//SR-IOV Capabilities
pci_read_config_dword(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_CAP, &iov->cap);
//The programming model for a Device may have vendor specific dependencies between sets of
//Functions. The Function Dependency Link field is used to describe these dependencies
pci_read_config_byte(dev, pos + PCI_SRIOV_FUNC_LINK, &iov->link);
if (pci_pcie_type(dev) == PCI_EXP_TYPE_RC_END)
iov->link = PCI_DEVFN(PCI_SLOT(dev->devfn), iov->link);
if (pdev)
iov->dev = pci_dev_get(pdev);
else
iov->dev = dev;
mutex_init(&iov->lock);
dev->sriov = iov;
dev->is_physfn = 1;
return 0;
failed:
for (i = 0; i < PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS; i++) {
res = dev->resource + PCI_IOV_RESOURCES + i;
res->flags = 0;
}
return rc;
}
开启SR-IOV
参考 ixgbe-4.3.15源码 ixgbe_init_module–>pci_register_driver(&ixgbe_driver), 当探测到有相应的pci设备时,就会调用ixgbe_driver.ixgbe_probe.
probe中会开启sr-iov:
if (adapter->flags & IXGBE_FLAG_SRIOV_CAPABLE) {
pci_sriov_set_totalvfs(pdev, IXGBE_MAX_VFS_DRV_LIMIT);
ixgbe_enable_sriov(adapter);
}
ixgbe_enable_sriov–>pci_enable_sriov–>sriov_enable
//要启用VF的个数,由用户传入
static int sriov_enable(struct pci_dev *dev, int nr_virtfn)
{
pci_read_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_INITIAL_VF, &initial);
if (initial > iov->total_VFs ||
(!(iov->cap & PCI_SRIOV_CAP_VFM) && (initial != iov->total_VFs)))
return -EIO;
if (nr_virtfn < 0 || nr_virtfn > iov->total_VFs ||
(!(iov->cap & PCI_SRIOV_CAP_VFM) && (nr_virtfn > initial)))
return -EINVAL;
pci_read_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_VF_OFFSET, &offset);
pci_read_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_VF_STRIDE, &stride);
if (!offset || (nr_virtfn > 1 && !stride))
return -EIO;
nres = 0;
for (i = 0; i < PCI_SRIOV_NUM_BARS; i++) {
bars |= (1 << (i + PCI_IOV_RESOURCES));
// 如果resouce有parent
res = dev->resource + PCI_IOV_RESOURCES + i;
if (res->parent)
nres++;
}
if (nres != iov->nres) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "not enough MMIO resources for SR-IOV\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
iov->offset = offset;
iov->stride = stride;
// VF bus number
if (virtfn_bus(dev, nr_virtfn - 1) > dev->bus->busn_res.end) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "SR-IOV: bus number out of range\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
if (pci_enable_resources(dev, bars)) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "SR-IOV: IOV BARS not allocated\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
if (iov->link != dev->devfn) {
pdev = pci_get_slot(dev->bus, iov->link);
if (!pdev)
return -ENODEV;
if (!pdev->is_physfn) {
pci_dev_put(pdev);
return -ENOSYS;
}
rc = sysfs_create_link(&dev->dev.kobj,
&pdev->dev.kobj, "dep_link");
pci_dev_put(pdev);
if (rc)
return rc;
}
pci_write_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_NUM_VF, nr_virtfn);
// 开启VFs
iov->ctrl |= PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_VFE | PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_MSE;
pci_cfg_access_lock(dev);
pci_write_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL, iov->ctrl);
msleep(100);
pci_cfg_access_unlock(dev);
iov->initial_VFs = initial;
if (nr_virtfn < initial)
initial = nr_virtfn; //initial为实际的VF 个数
for (i = 0; i < initial; i++) {
// 分配 一个VF Device ,并将VF Device 插入到当前设备bus的children链表的一个bus结点
// 的设备链表中, 最后启动Device对应的Driver
rc = virtfn_add(dev, i, 0);
if (rc)
goto failed;
}
kobject_uevent(&dev->dev.kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE);
iov->num_VFs = nr_virtfn; // VF的实际个数
return 0;
failed:
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
virtfn_remove(dev, j, 0);
iov->ctrl &= ~(PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_VFE | PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_MSE);
pci_cfg_access_lock(dev);
pci_write_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_CTRL, iov->ctrl);
pci_write_config_word(dev, iov->pos + PCI_SRIOV_NUM_VF, 0);
ssleep(1);
pci_cfg_access_unlock(dev);
if (iov->link != dev->devfn)
sysfs_remove_link(&dev->dev.kobj, "dep_link");
return rc;
}
VM使用VF
VMM只负责配置管理,避免参与到数据操作过程,体现了数据面与控制面分离思想。硬件通过映射表,实现VM直接与IO设备的数据 交互2。
通过以上操作可以将PCIe设备的VF开启,在创建Domain时,就可以通过配置文件将VF指定给VM,VM对PCIe设备的操作就是对此VF的BAR空间进行操作。Using SR-IOV
Intel 82599 SR-IOV Driver分析
VF 基本配置过程:
- 在 bios中启用vt-d功能
- 在xen启动项中添加引导参数: iommu=1 msi=1
- 在启动PF驱动时加载参数max_vfs=63,然后在pcilist中会发现虚拟网卡的BDF(eg: 0000:03:10.0)
- 利用pciback隐藏VM使用的虚拟网卡
- 在GuestOS的配置文件中增加:pci=[‘03:10.0’]
- GuestOS中加载 VF驱动
通过以上配置,VF就可以正常工作了3。
开启SR-IOV后收发数据流程
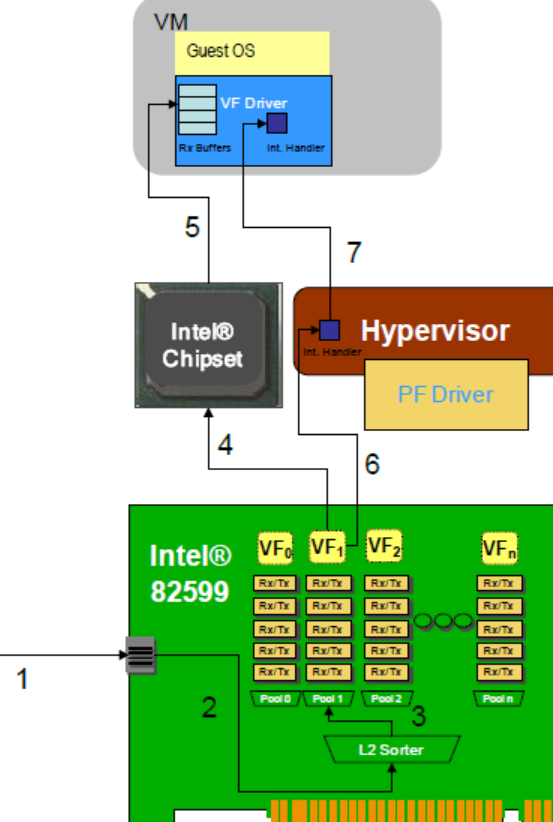
- 数据包到达网卡
- 被发送到L2交换层
- 基于目标MAC地址,包被分发到VF1
- 网卡提示DMA模块开始向VM传送数据
- DMA模块收到提示后,通过`VT-D技术(DMA地址重映射)得到所需的真实物理地址,然后开始传送数据
- 网卡发出中断提示接收工作已经完成,hypervisor接收到此中断
- hypervisor给 VM注入一个中断提示接收工作已经完成,然后VF驱动开始处理数据。
和VMDQ的异同:不同之处在于第五步,VMDQ需要Dom0参与DMA地址的重映射。
参考
-
Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing Specification Revision 1.1 ↩